Disabling orthostatic hypotension caused by sympathectomies performed for hyperhidrosis
J.J. van Lieshout, W. Wieling
Department of Medicine, Academic Medical Centre, University of Amsterdam, Amsterdam (The Netherlands)
An otherwise healthy 38 year-old woman suffered from severe hyperhidrosis of the hands and the feet since childhood, because of which she felt socially withdrawn. Since medical treatment of the hyperhidrosis proved ineffective, she was referred to a clinic for neurovegetative surgery. Extensive sympathectomies were performed over a period of two years, as summarized in Fig. 1. Following thoracoscopic sympathetic ganglionotomies bilaterally at the upper thoracic levels (Th II- Th VI), the excessive sweating of the hands disappeared. In the following year the procedure was extended to the lumbar levels L II - L IV at the left, while interganglionary sympathicotomies at LII - LIV at the right were performed with a salutary effect on plantar hyperhidrosis. After these procedures abnormal sweating developed, located at both dorsal and ventral parts of the trunk. A further right-sided extension of the sympathectomies was performed at the levels Th VII - Th XII, including a re-ganglionotomy at Th VI and an interganglionary sympathicotomy at Th X - Th XII. This resulted in relief of the hyperhidrosis over the right hemi-thorax. Abnormal sweating of the left side of the trunk persisted, while palmar hyperhidrosis returned on the left for which the following procedure was performed on the left side: re-ganglionotomy at Th II - Th V, a ganglionotomy at Th VII - Th IX and an interganglionary sympathicotomy at Th III, IV, XI and XII. Two days before the last procedure she had played a field hockey game in the highest veteran league, indicating an excellent exercise tolerance. Directly following the last operation she complained of dizziness on standing, causing her to become severely disabled preventing her acutely from performing housekeeping duties [1].
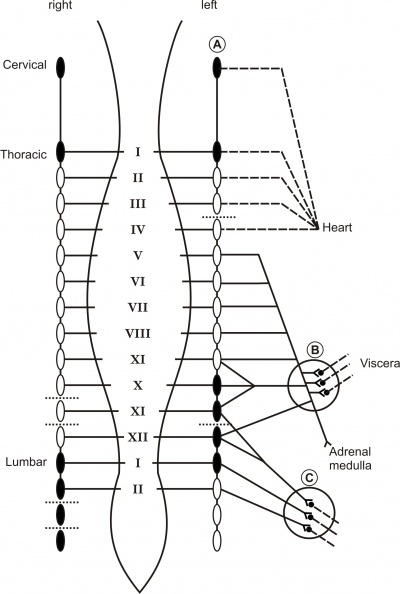
= postganglionic fibre 0 = intact sympathetic ganglion • = ganglionotomy A = cervical ganglia B = celiac and superior mesenteric ganglia C = lower abdominal sympathetic ganglia
Editor's comments
| Table 2:Typical Premonitory Symptoms for Reflex Syncope |
|---|
|
References
<biblio>
- Wieling pmid=15310717
<biblio>